Selected papers
|
Haussmann, I.U., Bodi, Z., Sanchez-Moran, E., Mongan, N., Archer, N., Fray, R., and Soller, M. (2016). m6A potentiates Sxl alternative pre-mRNA splicing for robust Drosophila sex determination. Nature 540:301-304.
Highlighted in Nature Chemical Biology’s News & Views section Highlighting article in Nature Reviews Genetics Highlighting article in Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology Press release: http://www.birmingham.ac.uk/schools/biosciences/news/2016/01Dec-determining-sex-in-fruit-flies.aspx |
|
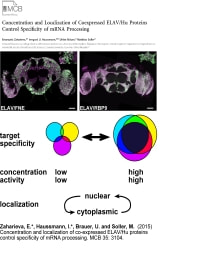
Zaharieva, E., Haussmann, I. U., Brauer, U. and Soller, M. (2015). Concentration and localization of co-expressed ELAV/Hu family proteins control specificity of mRNA processing. Mol. Cell. Biol. 35: 3104-3115.
|
|
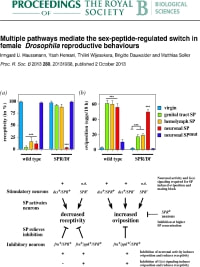
Haussmann, I. U., Hemani, Y., Wjiesekera, T., Dauwalder, B. and Soller, M. (2013). Multiple pathways mediate the sex-peptide-regulated switch in female Drosophila reproductive behaviors. Proceedings of the Royal Society B 280: 20131938.
|
|
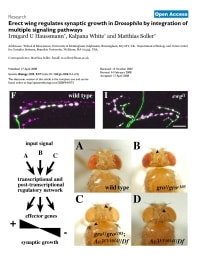
Haussmann, I.U., White, K. and Soller, M. (2008). Erect wing regulates synaptic growth in Drosophila by integration of multiple signaling pathways. Genome Biol. 9: 73.1-17.
Journal cover. |
|
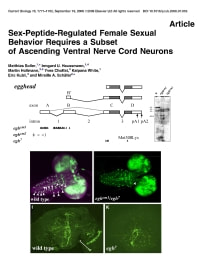
Soller, M., Haussmann, I.U., Hollmann, M., Choffat, Y., White, K., Kubli, E. and Schafer, M.A. (2006). Sex-peptide-regulated female sexual behavior requires a subset of ascending ventral nerve cord neurons. Curr. Biol. 16: 1771-1782.
Corresponding author. |
|
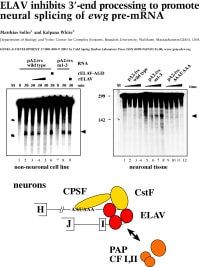
Soller, M. and White, K. (2003). ELAV inhibits 3' end formation to promote splicing of ewg pre-mRNA. GenesDev. 17: 2526-2538. Corresponding author.
|
Covers
Publications
Haussmann, I.U., Dix, T.C., Dezi, V., Hans, A., Arnold, R. and Soller, M. (2024) sgRNA structural constraints and genetic limitations for efficient Cas9 genome editing. BioRxiv.
Associated online tool: https://platinum-crispr.bham.ac.uk/predict.pl
McQuarrie, D.W.J., Alizada, A., Czech Nicholson, B. and Soller, M. (2024) Promoters of germline transposon silencing genes evolve rapidly accompanied by diverging gene expression. BioRxiv .
Ustaoglu, P., McQuarrie, D., Rochet, A., Haussmann, I.U., Dix, T.C., Devaud J.M., Arnold, R. and Soller, M. (2024) Memory consolidation in honey bees is enhanced by down-regulation of Down Syndrome Cell Adhesion Molecule and changes its alternative splicing. Frontiers of Molecular Neuroscience 16: 1322808.
Anreiter, I., Tian, Y. W. and Soller, M. (2023) The cap epitranscriptome: Early directions to a complex life as mRNA. BioEssays, 45: e2200198.
McQuarrie, D.W.J., Read, A.M., Stephens, F.H.S., Civetta, A. and Soller, M. (2023) Indel driven rapid evolution of core nuclear pore protein gene promoters. Scientific Reports 13: 8035.
Dix, T., Haussmann, I.U., Brivio, S., Nallasivan, M.P., Hadzhiev, Y., Muller, F., Muller, B., Pettitt, J. and Soller, M. (2022) CMTr mediated 2`-O-ribose methylation status of cap adjacent-nucleotides in animals. RNA 28:1377-90.
Haussmann, I.U., Wu, Y., Nallasivan, M.P., Archer, N., Bodi, Z., Hebenstreit, D., Waddell, S., Fray, R., and Soller, M.(2022) CMTr cap-adjacent 2`-O-ribose mRNA methyltransferases are required for reward learning and mRNA localization to synapses. Nature Communications, 13: 1209.
Press release.
Torres-Méndez, A., Pop, S., Bonnal, S., Almudi, I., Roberts, R.J., Paolantoni, C., Alcaina, A., Avola, A., Martín-Anduaga, A., Haussmann, I.U., Morin, V., Casares, F., Soller, M., Kadener, S., Roignant, JY., Prieto-Godino, L., and Irimia, M. (2022) Parallel evolution of a splicing program controlling neuronal excitability in flies and mammals. Science Advances, 8: eabk0445.
Ustaoglu, P., Gill, J.K., Doubovetzky, N., Haussmann, I.U., Dix, T.C., Arnold, R., Devaud J.M. and Soller, M. (2021) Dynamically expressed ELAV is required for learning and memory in bees. Communications Biology, 4: 1234.
Nallasivan, M.P., Haussmann, I.U., Civetta, A. and Soller, M. (2021). Channel nuclear pore protein 54 directs sexual differentiation and neuronal wiring required of female reproductive behaviors in Drosophila. BMC Biology, 19: 226.
Press release.
Bawankar, P., Lence, T., Paolantoni, C., Haussmann, I.U., Kazlauskiene, M., Jacob, D., Heidelberger, J., Richter, F., Nallasivan, M.P., Morin, V., Kreim, N., Beli, P., Helm, M., Jinek, M., Soller*, M. and Roignant*, JY (2021) Hakai is required for stabilizing core components of the m6A mRNA methylation machinery. Nature Communications, 12: 3778.
Munafo, M. Passera, A., Lawless, V.R., MacMillan, S., Bornelöv, S., Haussmann, I.U., Soller, M., Hannon, G.J. and Czech, B. (2021) Dedication of nuclear pore complex subunits to transposon silencing in Drosophila. eLIFE e66321.
Decio, P., Ustaoglu, P., Derecka, K., Hardy, I.C.W., Roat, T.C., Malaspina, O., Mongan, N., Stöger, R. and Soller, M.(2021) Thiamethoxam exposure in bees deregulates short ORF gene expression and compromises immune response to bacteria. Scientific Reports 11:1489.
Anreiter, I., Mir, Q., Simpson, J.T., Janga, S.C. and Soller (2021). New twists in detecting mRNA modification dynamics. Trends in Biotechnology. 39: 72-89.
Press release.
Wei, L., Lee, S., Majumdar, S., Zhang, B., Sanfilippo, P., Joseph, B., Miura, P., Soller, M. and Lai E.C. (2020) Overlapping activities of ELAV/Hu family RNA binding proteins specify the extended neuronal 3’ UTR landscape in Drosophila. Molecular Cell, 80: 140-155.
Singh, A.K., Abdullahi, A., Soller, M., David, A. and Brogna, S. (2020). Visualisation of ribosomes in Drosophila axons using Ribo-BiFC. Open Biology 8, 12, bio047233.
Decio, P., Ustaoglu, P., Roat, T.C., Malaspina, O., Devaud, J.M, Stöger, R. and Soller, M. (2019). Acute Thiamethoxam toxicity in honeybees is not enhanced by common fungicide and herbicide and lacks stress-induced changes in mRNA splicing. Scientific Reports 9: 19196.
Ustaoglu, P., Haussmann, I.U., Torres-Mendez, A., Liao, H., Arnold, R., Irimia, M. and Soller, M. (2019). Srrm234, but not canonical SR and hnRNP proteins drive inclusion of Down Syndrome Cell Adhesion Molecule exon 9 variable exons. RNA 25: 1353-65.
Soller, M. and Fray, R.G. (2019). RNA modifications in gene expression control. BBA Gene Regulatory Mechanism. 1862: 219-221.
Invited editorial for guest-edited special issue.
Torres-Mendez, A., Bonnal, S., Marquez, Y., Roth, J., Iglesias, M., Permanyer, J., Almudi, I., O’Hanlon, D., Guitart, T., Soller, M., Gingras, A. C., Gebauer, F., Rentzsch, F., Blencowe, B. J., Valcarcel, J. and Irimia, M. (2019). A novel protein domain drove the emergence of neural microexons in bilaterian animals. Nature Ecol Evol. 3: 691-701.
Balacco, D.L. and Soller, M. (2019) The m6A writer: Rise of a machine for growing tasks. Biochemistry 58: 363-378.
Haussmann, I. U., Ustaoglu, P., Brauer, U., Hemani, Y., Dix, T. and Soller, M. (2019). Plasmid-based gap-repair recombineered transgenes reveal a central role for introns in mutually exclusive alternative splicing of Down Syndrome Cell Adhesion Molecule exon 4. NAR 47:1389-1403.
Solomon, D.A., Stepto, A., Au, W.H., Adachi, Y., Diaper, D.C., Hall, R., Rekhi, A., Boudi, A., Lee, Y., Smith, B., Bridi, J., Spinelli, G., Dearlove, J., Humphrey, D.M., Gallo, J.M., Troakes, C., Fanto, M., Soller, M., Parsons, R., Hortobagyi, T., Shaw, E.C and Hirth, F. (2018). A feedback loop between dipeptide repeat protein, TDP-43 and Karyopherin-alpha mediates C9ORF72-related neurodegeneration. Brain 114: 2908-2924.
Knuckles, P., Lence, T., Haussmann, I.U., Jacob, D., Kreim, N., Carl, S.H., Masiello, I., Hares, T., Villasenor, R., Hess, D., Andrade-Navarro, M.A., Biggiogera, M., Helm, M., Soller, M., Buhler, M. and Roignant, J.Y. (2018). Zc3h13/Flacc is required for adenosine methylation by bridging the mRNA binding factor Rbm15/Spenito to the m6A machinery component Wtap/Fl(2)d. Genes&Development 32: 415-429.
Roignant, JY and Soller, M. (2017). m6A in mRNA: An ancient mechanism for fine-tuning gene expression. Opinion Article. Trends in Genetics 33: 380-90.
Recommended by Faculty of 1000.
Lence, T. Soller, M. and Roignant, JY (2017). A fly view on the roles and mechanisms of the m6A mRNA modification and its players. RNA Biology 14: 1232-1240.
Haussmann, I.U., Bodi, Z., Sanchez-Moran, E., Mongan, N., Archer, N., Fray, R., and Soller, M. (2016). m6A potentiates Sxl alternative pre-mRNA splicing for robust Drosophila sex determination. Nature 540:301-304.
Dezi, V., Ivanov, C., Haussmann, I. U. and Soller, M. (2016). mRNA modifications and their role in development and disease. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 44: 1385-93.
Zaharieva, E., Haussmann, I. U., Brauer, U. and Soller, M. (2015). Concentration and localization of co-expressed ELAV/Hu family proteins control specificity of mRNA processing. Mol. Cell. Biol. 35: 3104-3115.
Journal cover.
Brauer, U., Zaharieva, E. and Soller, M. (2014). Regulation of ELAV/Hu RNA binding proteins by phosphorylation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 42:1147-51.
Haussmann, I. U., Hemani, Y., Wjiesekera, T., Dauwalder, B. and Soller, M. (2013). Multiple pathways mediate the sex-peptide-regulated switch in female Drosophila reproductive behaviors. Proceedings of the Royal Society B 280: 20131938.
Zaharieva, E., Chipman, K, and Soller, M. (2012). Alternative splicing interference by xenobiotics. Toxicology. 296: 1-12.
Hemani, Y. and Soller, M. (2012). Mechanisms of Drosophila Dscam mutually exclusive splicing regulation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 40: 804-9.
Haussmann, I. U., Li, M. and Soller, M. (2011). ELAV mediated 3’-end processing of ewg transcripts is evolutionary conserved despite sequence degeneration of the ELAV binding site. Genetics. 189: 97-107.
Haussmann, I.U. and Soller, M. (2010). Differential activity of EWG transcription factor isoforms identifies a subset of differentially regulated genes important for synaptic growth regulation. Dev. Biol. 348: 224-230.
Journal cover.
Soller, M., Li, M. and Haussmann, I.U. (2010). Determinants of ELAV gene-specific regulation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 38: 1122-4.
Haussmann, I.U., White, K. and Soller, M. (2008). Erect wing regulates synaptic growth in Drosophila by integration of multiple signaling pathways. Genome Biol. 9: 73.1-17.
Journal cover.
Soller, M., Li, M. and Haussmann, I.U. (2008). Regulation of the ELAV target ewg: insights from an evolutionary perspective. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 36: 502-504.
Soller, M., Haussmann, I.U., Hollmann, M., Choffat, Y., White, K., Kubli, E. and Schafer, M.A. (2006). Sex-peptide-regulated female sexual behavior requires a subset of ascending ventral nerve cord neurons. Curr. Biol. 16: 1771-1782.
Corresponding author.
Soller, M. (2006). Pre-messengerRNA processing and its regulation: A genomic perspective. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 63: 796-819.
Fan, Y., Soller, M., Flister, S. Hollmann, M., Müller, M., Bello, B., Egger, B., White, K., Schafer, M.A. and Reichert, H. (2005). The egghead gene is required for compartment boundary formation in Drosophila optic lobe development. Dev. Biol. 287: 61-73.
Soller, M. and White, K. (2005). ELAV multimerizes on conserved AU4-6 motifs important for ewg splicing regulation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 25: 7580-7591.
Corresponding author.
Soller, M. and White, K. (2004). ELAV. Curr. Biol. 14: R53.
Soller, M. and White, K. (2003). ELAV inhibits 3' end formation to promote splicing of ewg pre-mRNA. GenesDev. 17: 2526-2538.
Corresponding author.
Saudan, P., Hauck, K., Soller, M., Choffat, Y., Ottiger, M., Spörri, M., Ding, Z., Hess, D., Gehrig, P. M., Klauser, S., Hunziker, P. and Kubli, E. (2002). Ductus ejaculatoris peptide 99B (DUP99B), a novel Drosophila melanogaster sex-peptide pheromone. Eur. J. Biochem., 269: 989-997.
Journal cover.
Koushika*, S. P., Soller*, M. and White K. (2000). The neuron-enriched splicing pattern of Drosophila erect wing is dependant on the presence of ELAV protein. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20: 1836-1845.
*equally contributing authors
Ottiger, M., Soller, M., Stocker, R. F. and Kubli, E. (2000). Binding sites of Drosophila melanogaster sex peptide pheromones. J. Neurobiol. 44: 57-71.
Journal cover.
Koushika, S. P., Soller, M., DeSimone, S. M., Daub, D. M. and White K. (1999). Differential and inefficient splicing of a broadly expressed Drosophila erect wing transcript results in tissue-specific enrichment of the vital EWG protein isoform. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19: 3998-4007.
Soller, M., Bownes, M. and Kubli, E. (1999). Control of oocyte maturation in sexually mature Drosophila females. Dev. Biol. 208: 337-351.
Soller, M., Bownes, M. and Kubli, E. (1997). Mating and sex-peptide stimulate the accumulation of yolk in oocytes of D. melanogaster. Eur. J. Biochem. 243: 732-738.
Soller, M. and Lanzrein, B. (1996). Polydnavirus and venom of the egg-larval parasitoid Chelonus inanitus(Braconidae) induce developmental arrest in the prepupa of its host Spodoptera littoralis (Noctuidae). J. Insect Physiol. 42: 471-481.
Associated online tool: https://platinum-crispr.bham.ac.uk/predict.pl
McQuarrie, D.W.J., Alizada, A., Czech Nicholson, B. and Soller, M. (2024) Promoters of germline transposon silencing genes evolve rapidly accompanied by diverging gene expression. BioRxiv .
Ustaoglu, P., McQuarrie, D., Rochet, A., Haussmann, I.U., Dix, T.C., Devaud J.M., Arnold, R. and Soller, M. (2024) Memory consolidation in honey bees is enhanced by down-regulation of Down Syndrome Cell Adhesion Molecule and changes its alternative splicing. Frontiers of Molecular Neuroscience 16: 1322808.
Anreiter, I., Tian, Y. W. and Soller, M. (2023) The cap epitranscriptome: Early directions to a complex life as mRNA. BioEssays, 45: e2200198.
McQuarrie, D.W.J., Read, A.M., Stephens, F.H.S., Civetta, A. and Soller, M. (2023) Indel driven rapid evolution of core nuclear pore protein gene promoters. Scientific Reports 13: 8035.
Dix, T., Haussmann, I.U., Brivio, S., Nallasivan, M.P., Hadzhiev, Y., Muller, F., Muller, B., Pettitt, J. and Soller, M. (2022) CMTr mediated 2`-O-ribose methylation status of cap adjacent-nucleotides in animals. RNA 28:1377-90.
Haussmann, I.U., Wu, Y., Nallasivan, M.P., Archer, N., Bodi, Z., Hebenstreit, D., Waddell, S., Fray, R., and Soller, M.(2022) CMTr cap-adjacent 2`-O-ribose mRNA methyltransferases are required for reward learning and mRNA localization to synapses. Nature Communications, 13: 1209.
Press release.
Torres-Méndez, A., Pop, S., Bonnal, S., Almudi, I., Roberts, R.J., Paolantoni, C., Alcaina, A., Avola, A., Martín-Anduaga, A., Haussmann, I.U., Morin, V., Casares, F., Soller, M., Kadener, S., Roignant, JY., Prieto-Godino, L., and Irimia, M. (2022) Parallel evolution of a splicing program controlling neuronal excitability in flies and mammals. Science Advances, 8: eabk0445.
Ustaoglu, P., Gill, J.K., Doubovetzky, N., Haussmann, I.U., Dix, T.C., Arnold, R., Devaud J.M. and Soller, M. (2021) Dynamically expressed ELAV is required for learning and memory in bees. Communications Biology, 4: 1234.
Nallasivan, M.P., Haussmann, I.U., Civetta, A. and Soller, M. (2021). Channel nuclear pore protein 54 directs sexual differentiation and neuronal wiring required of female reproductive behaviors in Drosophila. BMC Biology, 19: 226.
Press release.
Bawankar, P., Lence, T., Paolantoni, C., Haussmann, I.U., Kazlauskiene, M., Jacob, D., Heidelberger, J., Richter, F., Nallasivan, M.P., Morin, V., Kreim, N., Beli, P., Helm, M., Jinek, M., Soller*, M. and Roignant*, JY (2021) Hakai is required for stabilizing core components of the m6A mRNA methylation machinery. Nature Communications, 12: 3778.
Munafo, M. Passera, A., Lawless, V.R., MacMillan, S., Bornelöv, S., Haussmann, I.U., Soller, M., Hannon, G.J. and Czech, B. (2021) Dedication of nuclear pore complex subunits to transposon silencing in Drosophila. eLIFE e66321.
Decio, P., Ustaoglu, P., Derecka, K., Hardy, I.C.W., Roat, T.C., Malaspina, O., Mongan, N., Stöger, R. and Soller, M.(2021) Thiamethoxam exposure in bees deregulates short ORF gene expression and compromises immune response to bacteria. Scientific Reports 11:1489.
Anreiter, I., Mir, Q., Simpson, J.T., Janga, S.C. and Soller (2021). New twists in detecting mRNA modification dynamics. Trends in Biotechnology. 39: 72-89.
Press release.
Wei, L., Lee, S., Majumdar, S., Zhang, B., Sanfilippo, P., Joseph, B., Miura, P., Soller, M. and Lai E.C. (2020) Overlapping activities of ELAV/Hu family RNA binding proteins specify the extended neuronal 3’ UTR landscape in Drosophila. Molecular Cell, 80: 140-155.
Singh, A.K., Abdullahi, A., Soller, M., David, A. and Brogna, S. (2020). Visualisation of ribosomes in Drosophila axons using Ribo-BiFC. Open Biology 8, 12, bio047233.
Decio, P., Ustaoglu, P., Roat, T.C., Malaspina, O., Devaud, J.M, Stöger, R. and Soller, M. (2019). Acute Thiamethoxam toxicity in honeybees is not enhanced by common fungicide and herbicide and lacks stress-induced changes in mRNA splicing. Scientific Reports 9: 19196.
Ustaoglu, P., Haussmann, I.U., Torres-Mendez, A., Liao, H., Arnold, R., Irimia, M. and Soller, M. (2019). Srrm234, but not canonical SR and hnRNP proteins drive inclusion of Down Syndrome Cell Adhesion Molecule exon 9 variable exons. RNA 25: 1353-65.
Soller, M. and Fray, R.G. (2019). RNA modifications in gene expression control. BBA Gene Regulatory Mechanism. 1862: 219-221.
Invited editorial for guest-edited special issue.
Torres-Mendez, A., Bonnal, S., Marquez, Y., Roth, J., Iglesias, M., Permanyer, J., Almudi, I., O’Hanlon, D., Guitart, T., Soller, M., Gingras, A. C., Gebauer, F., Rentzsch, F., Blencowe, B. J., Valcarcel, J. and Irimia, M. (2019). A novel protein domain drove the emergence of neural microexons in bilaterian animals. Nature Ecol Evol. 3: 691-701.
Balacco, D.L. and Soller, M. (2019) The m6A writer: Rise of a machine for growing tasks. Biochemistry 58: 363-378.
Haussmann, I. U., Ustaoglu, P., Brauer, U., Hemani, Y., Dix, T. and Soller, M. (2019). Plasmid-based gap-repair recombineered transgenes reveal a central role for introns in mutually exclusive alternative splicing of Down Syndrome Cell Adhesion Molecule exon 4. NAR 47:1389-1403.
Solomon, D.A., Stepto, A., Au, W.H., Adachi, Y., Diaper, D.C., Hall, R., Rekhi, A., Boudi, A., Lee, Y., Smith, B., Bridi, J., Spinelli, G., Dearlove, J., Humphrey, D.M., Gallo, J.M., Troakes, C., Fanto, M., Soller, M., Parsons, R., Hortobagyi, T., Shaw, E.C and Hirth, F. (2018). A feedback loop between dipeptide repeat protein, TDP-43 and Karyopherin-alpha mediates C9ORF72-related neurodegeneration. Brain 114: 2908-2924.
Knuckles, P., Lence, T., Haussmann, I.U., Jacob, D., Kreim, N., Carl, S.H., Masiello, I., Hares, T., Villasenor, R., Hess, D., Andrade-Navarro, M.A., Biggiogera, M., Helm, M., Soller, M., Buhler, M. and Roignant, J.Y. (2018). Zc3h13/Flacc is required for adenosine methylation by bridging the mRNA binding factor Rbm15/Spenito to the m6A machinery component Wtap/Fl(2)d. Genes&Development 32: 415-429.
Roignant, JY and Soller, M. (2017). m6A in mRNA: An ancient mechanism for fine-tuning gene expression. Opinion Article. Trends in Genetics 33: 380-90.
Recommended by Faculty of 1000.
Lence, T. Soller, M. and Roignant, JY (2017). A fly view on the roles and mechanisms of the m6A mRNA modification and its players. RNA Biology 14: 1232-1240.
Haussmann, I.U., Bodi, Z., Sanchez-Moran, E., Mongan, N., Archer, N., Fray, R., and Soller, M. (2016). m6A potentiates Sxl alternative pre-mRNA splicing for robust Drosophila sex determination. Nature 540:301-304.
Dezi, V., Ivanov, C., Haussmann, I. U. and Soller, M. (2016). mRNA modifications and their role in development and disease. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 44: 1385-93.
Zaharieva, E., Haussmann, I. U., Brauer, U. and Soller, M. (2015). Concentration and localization of co-expressed ELAV/Hu family proteins control specificity of mRNA processing. Mol. Cell. Biol. 35: 3104-3115.
Journal cover.
Brauer, U., Zaharieva, E. and Soller, M. (2014). Regulation of ELAV/Hu RNA binding proteins by phosphorylation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 42:1147-51.
Haussmann, I. U., Hemani, Y., Wjiesekera, T., Dauwalder, B. and Soller, M. (2013). Multiple pathways mediate the sex-peptide-regulated switch in female Drosophila reproductive behaviors. Proceedings of the Royal Society B 280: 20131938.
Zaharieva, E., Chipman, K, and Soller, M. (2012). Alternative splicing interference by xenobiotics. Toxicology. 296: 1-12.
Hemani, Y. and Soller, M. (2012). Mechanisms of Drosophila Dscam mutually exclusive splicing regulation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 40: 804-9.
Haussmann, I. U., Li, M. and Soller, M. (2011). ELAV mediated 3’-end processing of ewg transcripts is evolutionary conserved despite sequence degeneration of the ELAV binding site. Genetics. 189: 97-107.
Haussmann, I.U. and Soller, M. (2010). Differential activity of EWG transcription factor isoforms identifies a subset of differentially regulated genes important for synaptic growth regulation. Dev. Biol. 348: 224-230.
Journal cover.
Soller, M., Li, M. and Haussmann, I.U. (2010). Determinants of ELAV gene-specific regulation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 38: 1122-4.
Haussmann, I.U., White, K. and Soller, M. (2008). Erect wing regulates synaptic growth in Drosophila by integration of multiple signaling pathways. Genome Biol. 9: 73.1-17.
Journal cover.
Soller, M., Li, M. and Haussmann, I.U. (2008). Regulation of the ELAV target ewg: insights from an evolutionary perspective. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 36: 502-504.
Soller, M., Haussmann, I.U., Hollmann, M., Choffat, Y., White, K., Kubli, E. and Schafer, M.A. (2006). Sex-peptide-regulated female sexual behavior requires a subset of ascending ventral nerve cord neurons. Curr. Biol. 16: 1771-1782.
Corresponding author.
Soller, M. (2006). Pre-messengerRNA processing and its regulation: A genomic perspective. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 63: 796-819.
Fan, Y., Soller, M., Flister, S. Hollmann, M., Müller, M., Bello, B., Egger, B., White, K., Schafer, M.A. and Reichert, H. (2005). The egghead gene is required for compartment boundary formation in Drosophila optic lobe development. Dev. Biol. 287: 61-73.
Soller, M. and White, K. (2005). ELAV multimerizes on conserved AU4-6 motifs important for ewg splicing regulation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 25: 7580-7591.
Corresponding author.
Soller, M. and White, K. (2004). ELAV. Curr. Biol. 14: R53.
Soller, M. and White, K. (2003). ELAV inhibits 3' end formation to promote splicing of ewg pre-mRNA. GenesDev. 17: 2526-2538.
Corresponding author.
Saudan, P., Hauck, K., Soller, M., Choffat, Y., Ottiger, M., Spörri, M., Ding, Z., Hess, D., Gehrig, P. M., Klauser, S., Hunziker, P. and Kubli, E. (2002). Ductus ejaculatoris peptide 99B (DUP99B), a novel Drosophila melanogaster sex-peptide pheromone. Eur. J. Biochem., 269: 989-997.
Journal cover.
Koushika*, S. P., Soller*, M. and White K. (2000). The neuron-enriched splicing pattern of Drosophila erect wing is dependant on the presence of ELAV protein. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20: 1836-1845.
*equally contributing authors
Ottiger, M., Soller, M., Stocker, R. F. and Kubli, E. (2000). Binding sites of Drosophila melanogaster sex peptide pheromones. J. Neurobiol. 44: 57-71.
Journal cover.
Koushika, S. P., Soller, M., DeSimone, S. M., Daub, D. M. and White K. (1999). Differential and inefficient splicing of a broadly expressed Drosophila erect wing transcript results in tissue-specific enrichment of the vital EWG protein isoform. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19: 3998-4007.
Soller, M., Bownes, M. and Kubli, E. (1999). Control of oocyte maturation in sexually mature Drosophila females. Dev. Biol. 208: 337-351.
Soller, M., Bownes, M. and Kubli, E. (1997). Mating and sex-peptide stimulate the accumulation of yolk in oocytes of D. melanogaster. Eur. J. Biochem. 243: 732-738.
Soller, M. and Lanzrein, B. (1996). Polydnavirus and venom of the egg-larval parasitoid Chelonus inanitus(Braconidae) induce developmental arrest in the prepupa of its host Spodoptera littoralis (Noctuidae). J. Insect Physiol. 42: 471-481.
Proudly powered by Weebly