Current projects
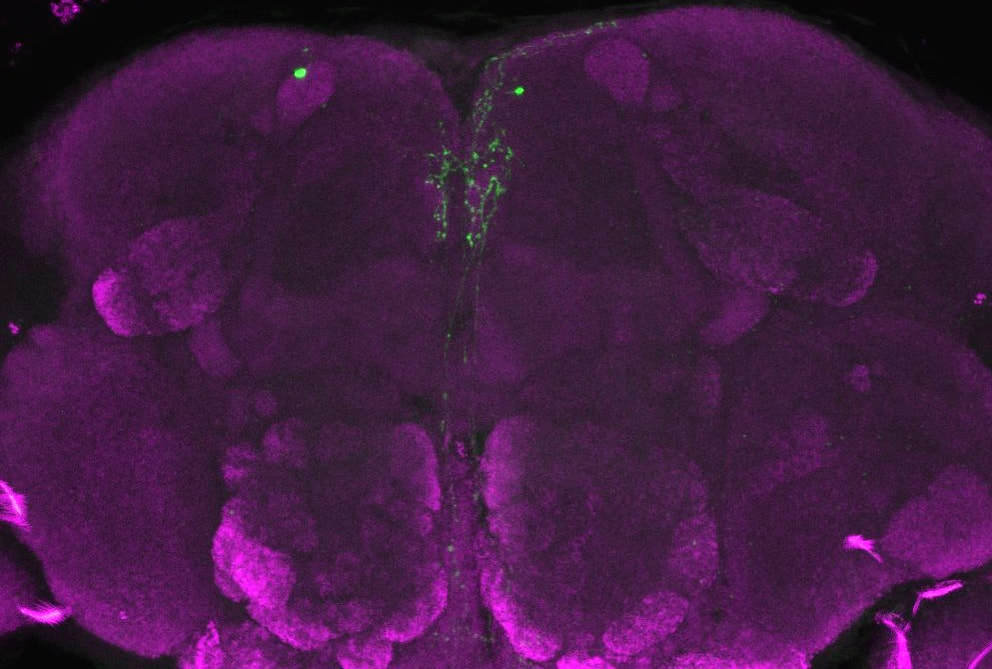
Messenger RNA methylation
|
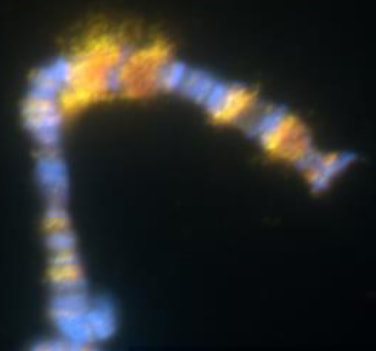
Alternative splicing: ELAV
|
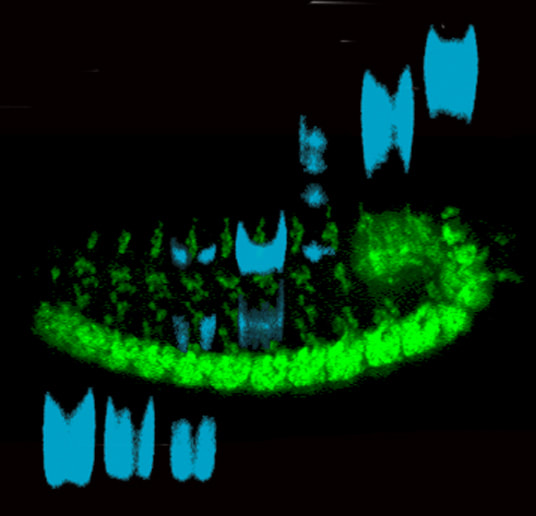
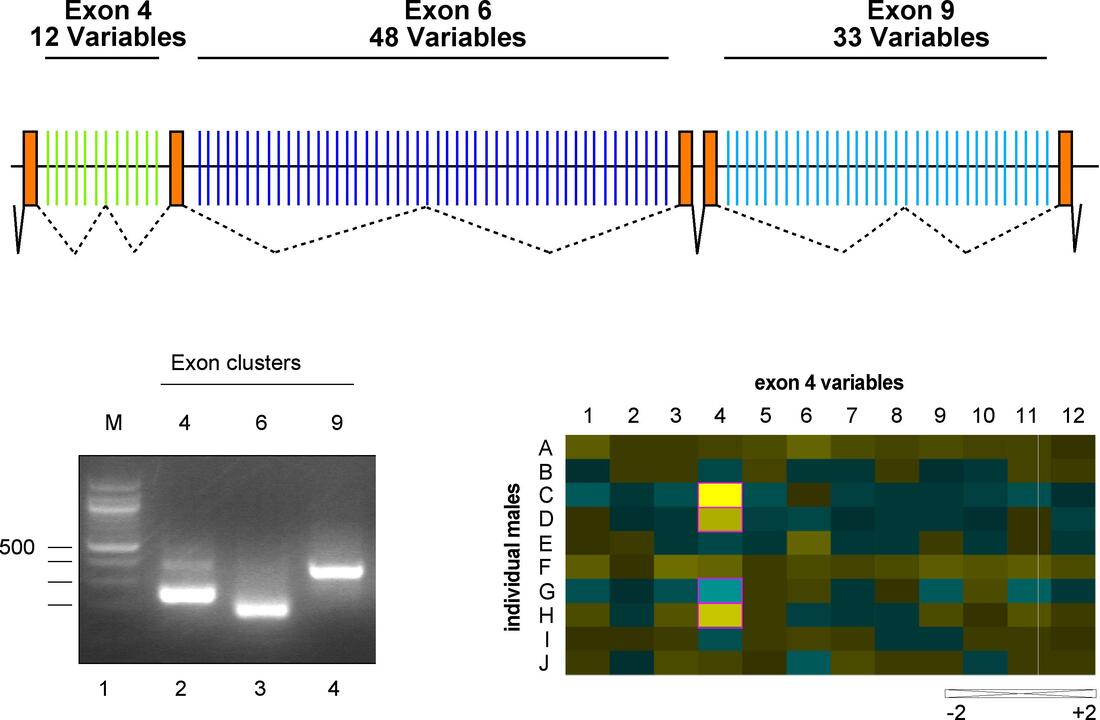
Alternative splicing: DSCAM
|
Drosophila post-mating response
|
Proudly powered by Weebly